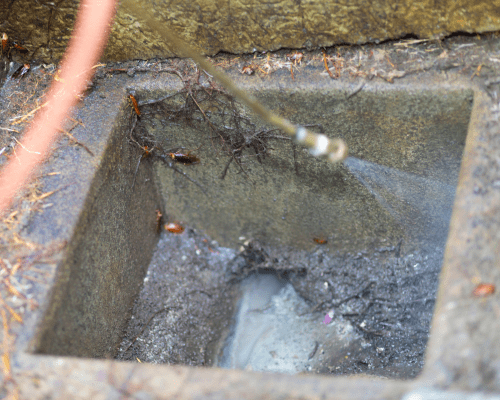
Cockroaches

They're those little brown, bacteria-filled bugs that run around your kitchen in the middle of the night and have a much longer history than you might think.
But what do we really know about cockroaches? Let's take a closer look at these hardy creatures and why it's crucial to keep them in check.
What do you need to know about cockroaches?
Origin
Cockroaches are one of the oldest insects in existence, with a line of descent dating back more than 320 million years. They are believed to have originated on the African continent, from where they spread to all parts of the world, adapting to diverse climatic and environmental conditions.
Resistance
They are known for their impressive resilience. They can survive without food for over a month, without water for a week and, even more surprisingly, without a head for a week (they actually die of thirst). Their ability to adapt to a variety of adverse conditions makes them one of the most difficult pests to control and eradicate, but not impossible.
Where there's one, there's a hundred
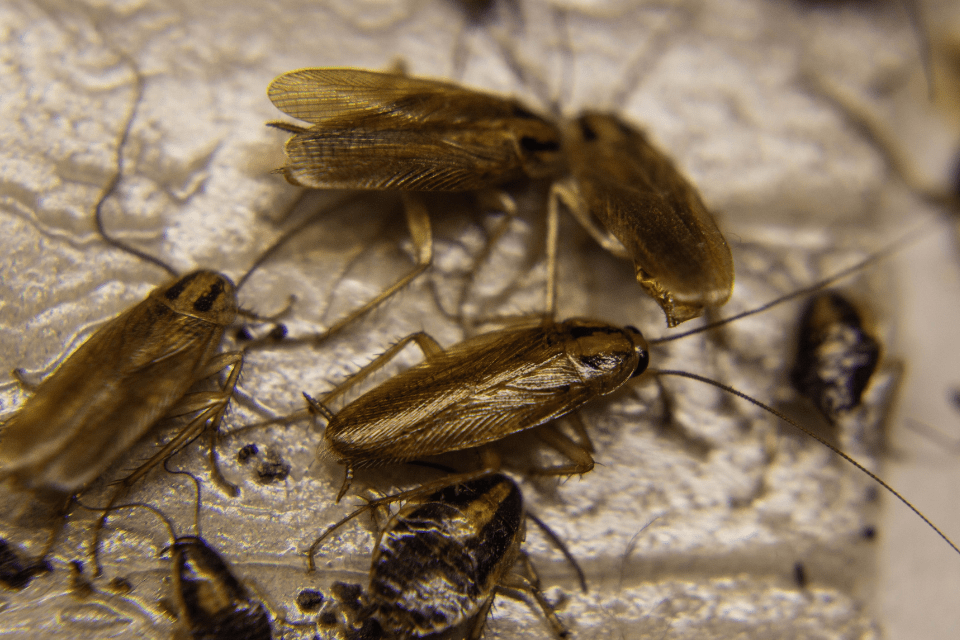
A single cockroach seen in your home can be indicative of a much larger infestation hiding in cracks and crevices. They reproduce rapidly, which means that a small colony can become a sizeable infestation in a short period of time and infest an entire building in a matter of weeks.
Health risks
Cockroaches can transmit dangerous bacteria such as E. coli and Salmonella, which can result in foodborne illness. In addition, their waste and shed skins may trigger allergic reactions and asthma, especially in children.
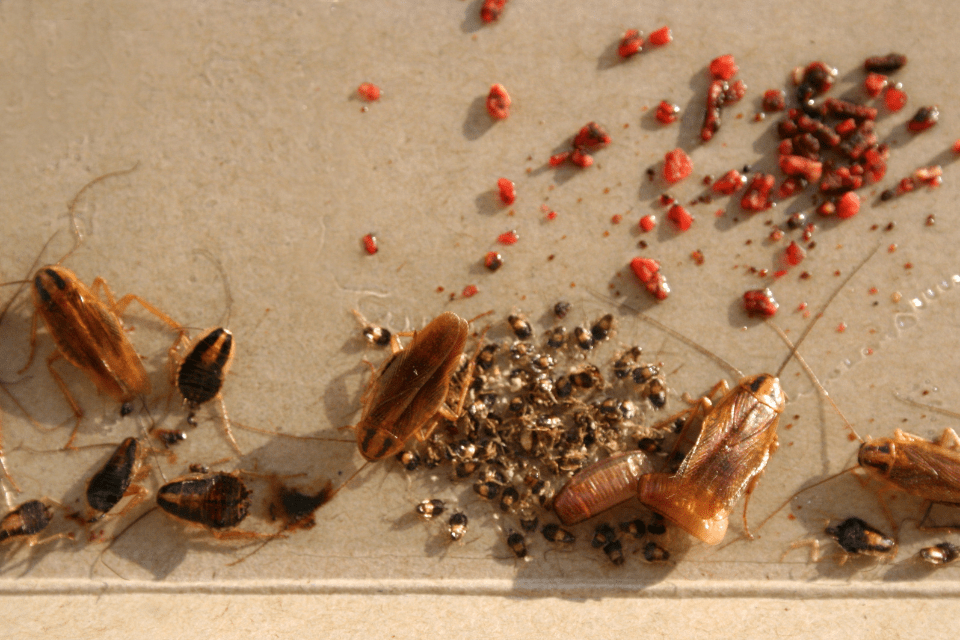


Do cockroaches bite?
No, cockroaches do not bite, but they do bite, and with a force 50 times their weight. Compared to a human bite, it is up to five times stronger. It can cause redness and swelling in the area of the bite.
The problem of common insecticides

Aerosols
Common insecticide sprays may provide instant gratification at seeing the cockroach drop, but they are not effective in treating an infestation at its root. In addition, these chemicals can be harmful if inhaled or come into contact with the skin.

The health of your family and pets
Insecticides can be hazardous to children and pets, who may be exposed to chemical residues left behind after application.

Cockroaches develop immunity
Over time, cockroaches can develop resistance to insecticides, making these methods less effective and requiring stronger doses or different formulations to maintain efficacy.
The importance of hiring professional fumigators
Hiring Fumigation FuerteventuraWe guarantee you an effective and safe elimination of cockroaches. We use harmless methods such as cold cryodisinfestation that are safe for your family and pets, and are designed to eradicate a cockroach infestation in a controlled and efficient manner.
Most common cockroaches in Fuerteventura
Germanic cockroach (Blattella germanica)

This is one of the most common species and is especially good at infiltrating buildings. They are small, light brown cockroaches and reproduce at an alarming rate.
American cockroach (Periplaneta americana)

The American cockroach is one of the largest cockroaches and is known for its ability to fly, making it many people's worst nightmare. They prefer warm, moist areas and can be difficult to eradicate once they have established a colony.
Oriental cockroach (Blatta orientalis)

Larger and darker in colour, the Oriental cockroach prefers damp and cool places. They are not as quick to reproduce as their Germanic cousins, but still pose a considerable threat.
Curiosities about cockroaches
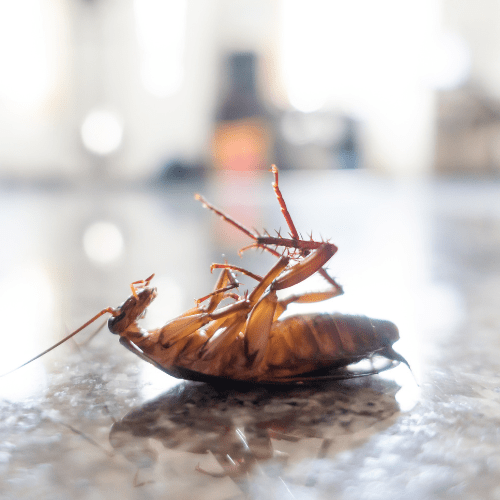
Cockroaches are flat-bodied, oval insects with six spiny legs and two long antennae. They vary in colour from light brown to black, depending on the species. They have a small head and a tough exoskeleton that allows them to slip easily through small cracks and crevices.
Some species of cockroaches have wings and can fly, although they are not very proficient in the air. The American cockroach is an example of a species that can fly, although they generally prefer to run if they need to escape from danger.
Although they can be a nuisance in our homes, cockroaches play an important role in the ecosystem. They help to break down organic matter, thus recycling nutrients in the soil. They can also be a source of food for other animals.
The size of cockroaches can vary greatly depending on the species. Some small species are only a few millimetres long, while the American cockroach can grow to about 4 centimetres in length.
Cockroaches can hold their breath for long periods of time, up to 40 minutes, but they cannot live underwater indefinitely. Eventually, they will drown if they cannot reach the surface to breathe.
Cockroaches are known for their resilience. They can survive without food for a month, without water for a week and, under ideal conditions, can live for around 15 months in the case of females. Males a little less.
This is a popular myth, but not entirely true. Cockroaches are more resistant to radiation than humans, but they would still die in a nuclear bomb blast or from the high doses of radiation that would follow. The idea of their nuclear survival comes from their ability to withstand higher levels of radiation compared to other organisms. There are insects that are much more resistant to radiation.




